Common Dental Problems And How To Prevent Them
Dental problems are a common occurrence that affects millions of people worldwide. From cavities to gum disease, these issues can cause discomfort, pain, and even tooth loss if left untreated. But the good news is that many of these dental problems are preventable with proper care and attention to oral hygiene.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the most common dental problems and how to prevent them. Whether you’re dealing with a toothache or simply looking to maintain good oral health, these tips and tricks will help keep your teeth and gums healthy and strong.
So, if you’re ready to take control of your dental health and prevent common dental problems, read on for some expert advice and practical tips.
What Are Common Dental Problems?
Dental problems are common concerns for most people, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. These dental problems range from mild oral health issues such as plaque buildup and bad breath to severe dental conditions such as gum disease and tooth decay. Understanding these common dental problems is crucial in maintaining proper dental hygiene, and preventing them is essential to avoid adverse effects on overall health.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common dental problem caused by bacteria in the mouth producing acid that damages the tooth enamel, leading to cavities. Tooth decay is prevalent in people of all ages and can cause toothaches, sensitivity, and visible holes or pits in the teeth. Understanding the causes and preventative measures of tooth decay can help maintain good oral health and prevent the need for extensive dental treatment.
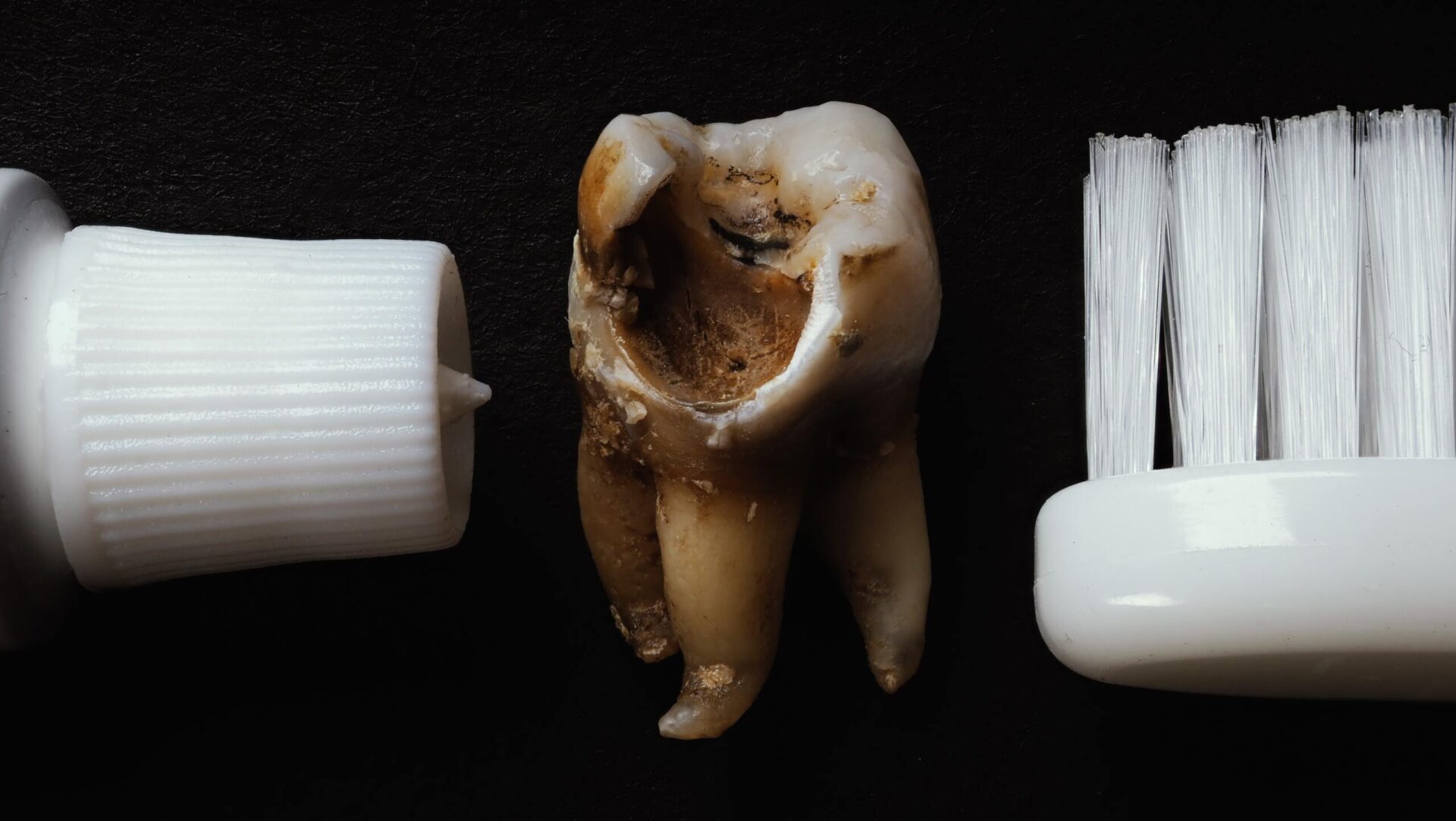
What Causes Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that affects people of all ages. This condition occurs when the hard, outer layer of our teeth known as enamel becomes damaged, leading to holes or cavities on the tooth surfaces. Tooth decay is caused by a build-up of bacteria on our teeth that creates a sticky film known as plaque, which over time, can cause enamel damage.
The process of tooth decay begins when we eat or drink sugary or starchy foods such as candy, soda, bread, or cereal. The bacteria in plaque feed on the sugars and carbohydrates in our food, producing acids that attack the enamel on our teeth. This process is known as demineralization, and it weakens the tooth structure over time, eventually leading to the formation of cavities.
Poor oral hygiene practices, such as irregular brushing or flossing, can lead to the build-up of plaque on our teeth, increasing the risk of tooth decay. Unhealthy diet choices, including frequent consumption of sugary or starchy foods, and drinks, also contribute to the development of tooth decay.
In addition to these factors, genetics also play a role in the likelihood of tooth decay. Some people are more susceptible to enamel damage due to inherited traits that affect their saliva pH levels or tooth structure.
How Can I Prevent Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is a common dental problem caused by the buildup of plaque on teeth and the demineralization of tooth enamel due to acid production from bacteria in the plaque. Fortunately, it’s a preventable condition. Here are some tips on how to prevent tooth decay:
- Practice good dental hygiene
The most important step in preventing tooth decay is to practice good dental hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, preferably with fluoride toothpaste, to remove any plaque buildup and strengthen your tooth enamel. Daily flossing is also crucial to remove any food particles that may be stuck between teeth and can’t be reached with a toothbrush.
- Watch your diet
Your diet also plays a significant role in preventing tooth decay. Limit consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, which can weaken tooth enamel and promote bacterial growth. Instead, opt for a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium-rich foods to help keep your teeth strong and avoid calcium deficiency.
- Drink plenty of water
Drinking water can help rinse away any leftover debris in your mouth, preventing the buildup of plaque on teeth.
- Visit your dentist regularly
Regular dental visits are crucial in preventing tooth decay. A dentist can identify and treat any oral health issues before they become more severe. They may also recommend fluoride varnishes or provide advice on preventive measures like sealants.
Tooth Enamel Loss
Tooth enamel loss is a common dental problem that occurs when the hard outer layer of the tooth, called the enamel, erodes or wears away. This enamel serves as a barrier protecting the tooth from damage and decay. Enamel loss can be caused by a variety of factors such as acidic foods and drinks, dry mouth, teeth grinding, and bacterial plaque buildup. Once tooth enamel is lost, it cannot be replaced, making it essential to prevent further damage and take steps to protect the teeth.

What Causes Tooth Enamel Loss?
Tooth enamel is the hard, outermost layer of our teeth. It acts as a protective barrier against tooth decay and tooth sensitivity. However, as strong as it is, tooth enamel can be eroded over time and it does not come back once it is lost. Tooth enamel loss can occur for a number of reasons and can have detrimental effects on our oral health.
One of the main causes of tooth enamel loss is the consumption of sugary and acidic drinks. Sugary drinks such as soda or energy drinks, as well as acidic drinks like fruit juices or sports drinks, can wear down tooth enamel over time. These drinks create an acidic environment in your mouth, which can attack the enamel on your teeth and over time lead to erosion.
Frequent vomiting, as seen in people with eating disorders or acid reflux, can also cause tooth enamel loss. The stomach acid brought up during vomiting is highly acidic and can damage the enamel of the teeth, leading to erosion and tooth decay.
Another factor that can cause tooth enamel loss is inadequate dental hygiene practices. Brushing too hard with a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause abrasion on teeth, leading to enamel loss over time. In addition to brushing too hard, not brushing your teeth thoroughly or frequently enough can also lead to an accumulation of plaque on the surface of the tooth, which can erode enamel.
Lastly, some medications that reduce saliva production, like antihistamines, antidepressants, and antipsychotics, can also lead to tooth enamel loss because they leave the mouth dry and prone to bacteria.
Preventing tooth enamel loss involves establishing good dental hygiene practices. Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and a fluoride toothpaste can help prevent enamel loss. Additionally, avoiding sugary snacks and acidic drinks, and drinking plenty of water can help wash away any damaging acids in your mouth. Regular dental checkups and cleanings are also important for preventing tooth enamel loss and addressing any dental issues that may arise.
How Can I Prevent Tooth Enamel Loss?
Tooth enamel is a vital part of your tooth’s structure, protecting it from decay and damage. Unfortunately, it can also wear down over time due to various factors, leading to cavities and sensitivity. In this article, we’ll discuss several steps you can take to prevent tooth enamel loss and maintain good oral health.
- Limit Your Consumption of Acidic Foods and Drinks
One of the primary causes of tooth enamel loss is exposure to acids, which can come from acidic foods and drinks like citrus fruits, soda, fruit juices, and vinegar-based dressings. These acids can soften your tooth enamel, making it more vulnerable to erosion and decay. Therefore, it’s essential to limit your intake of acidic beverages and foods and rinse your mouth with water after consuming them to neutralize the acids.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste
Fluoride is a mineral that can strengthen tooth enamel and make it more resistant to decay. It works by remineralizing the areas that have been damaged by acids or bacteria, keeping your teeth healthy and strong. Therefore, choosing a good-quality fluoride toothpaste and using it twice daily can help prevent tooth enamel loss. You can also use a fluoride mouthwash to boost enamel protection.
- Brush Gently, Not Hard
Some people believe that brushing their teeth with force can make them cleaner and whiter. However, this is a misconception that can actually damage your tooth enamel and gums. Brushing too hard can cause abrasion on your teeth, removing the enamel layer and exposing the dentin underneath. Therefore, it’s vital to brush gently using a soft-bristled toothbrush, applying just enough pressure to remove the plaque without scraping your enamel away.
- Use a Mouthguard
If you grind your teeth during sleep or while under stress, you can cause significant damage to your tooth enamel. Grinding or clenching your teeth puts excessive force on them, increasing the risk of cracks, chips, and wear. Therefore, using a mouthguard or splint can help protect your teeth from these forces and prevent enamel loss over time.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Lastly, visiting your dentist every six months is crucial to maintaining good oral health and preventing enamel loss. Your dentist can detect any signs of tooth decay or erosion early on and provide treatments such as fluoride varnishes, dental sealants, or root planning to prevent further damage. Moreover, regular cleanings can remove any plaque or tartar buildup that could erode your enamel and cause cavities.
Dry Mouth
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a common dental problem that occurs when the salivary glands in your mouth do not produce enough saliva to keep it moist. When your mouth is dry, it can become uncomfortable and make it difficult to speak, eat, or swallow. Moreover, dry mouth can increase the risk of dental decay, bacterial infections, and gum disease, as saliva has protective properties that neutralize acids, wash away food particles, and keep your oral tissues healthy. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and prevention of dry mouth to maintain good oral hygiene and overall health.

What Causes Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a condition in which the mouth fails to produce enough saliva to keep it moist. This can be uncomfortable and can also lead to various oral health problems. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of this condition.
One of the most common causes of dry mouth is the use of prescription medications. Some medications, such as those for high blood pressure, depression, anxiety, and allergies, have been found to reduce the flow of saliva. Other drugs that can lead to dry mouth include antihistamines, diuretics, and muscle relaxants.
Salivary gland disease is another common contributing factor to dry mouth. This disease can lead to the inability of the salivary glands to produce sufficient saliva. Nerve damage can also cause dry mouth; this can occur as a result of injury, illness, or surgery. Diabetes has also been linked to dry mouth, likely due to the changes in blood sugar levels affecting the production of saliva.
In addition to medical conditions, certain lifestyle factors can also lead to dry mouth. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake have been associated with reduced salivary flow. HIV/AIDS is another condition that can lead to dry mouth, particularly when it is advanced.
The elderly are more prone to developing dry mouth due to the normal aging process. As you age, your salivary glands may not function as well as they once did, leading to reduced saliva production. Finally, dehydration is another culprit that can cause dry mouth.
How Can I Prevent Dry Mouth?
Dry mouth is a common ailment caused by a reduction in the flow of saliva. It can lead to dental problems such as tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. Fortunately, there are a few steps you can take to help prevent dry mouth.
One way to prevent dry mouth is to ensure that you stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is crucial in keeping your mouth moisturized. Avoiding dehydrating substances such as alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, and sugary foods can also help prevent dry mouth from occurring.
To stimulate saliva production, try chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy. This can help keep your mouth moist and aid in the prevention of dry mouth.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice a day and flossing can also help prevent dry mouth and its related dental problems. Brushing and flossing can help to remove any food particles or plaque buildup that can exacerbate dry mouth.
If you are taking medications that may contribute to dry mouth, speak to your doctor about adjusting your prescription. Your doctor may be able to prescribe an alternative medication that does not cause a reduction in saliva flow.
Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental problem that occurs when the tooth enamel, the protective layer on the outside of the tooth, wears away, exposing the dentin layer underneath. This can result in discomfort or pain when the tooth is exposed to hot or cold temperatures, sweet or acidic substances, or even air. Tooth sensitivity can be a nuisance for many people, as it can interfere with eating and drinking normally. However, there are steps that can be taken to prevent and treat tooth sensitivity.

What Causes Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental problem that occurs when one experiences discomfort or pain in their teeth as a result of external stimuli such as cold or hot food and drinks, air, or sweet foods. Several factors cause tooth sensitivity, and knowing what triggers it can help you prevent it and protect your teeth.
One of the main reasons that cause tooth sensitivity is enamel erosion. Enamel is the outer layer of the teeth, and it protects the dentin, which is the sensitive layer underneath. Acidic foods and drinks can wear away the enamel, exposing the dentin and resulting in sensitivity. Enamel erosion can also result from frequent brushing or brushing too hard, leading to gum recession.
Gum recession is another factor that exposes the nerves in the teeth. When the gums pull away from the teeth, the dentin and nerves become exposed, leading to sensitivity. Several factors can cause gum recession, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, smoking, and genetics.
Tooth decay is also a common cause of tooth sensitivity. When tooth decay forms, it creates small holes in the teeth, exposing the dentin and nerves. The bacteria in the decay also create acid, which further damages the tooth enamel, resulting in sensitivity.
Acidic food and drinks such as citrus fruits, vinegar, and soda can also cause tooth sensitivity. The acid in these foods erodes the enamel and exposes the dentin, leading to sensitivity.
Besides these factors, tooth sensitivity can also result from teeth grinding, which wears away the enamel and exposes the underlying layers of the teeth. This condition, also known as bruxism, can be triggered by stress or anxiety.
Some risk factors may contribute to tooth sensitivity, including age, brushing habits, and genetics. Young adults and seniors are more likely to develop tooth sensitivity than other age groups. Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can also wear away the enamel, causing sensitivity. Genetics can also play a role, with some people being more prone to sensitivity regardless of their brushing habits.
How Can I Prevent Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity can be a painful and uncomfortable experience, but the good news is that it is preventable. Knowing the causes of tooth sensitivity is crucial to adopting preventive measures and reducing the risk of developing this condition. Here are some tips on how to prevent tooth sensitivity:
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear away the enamel and cause sensitivity. It is essential to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently to avoid damaging the enamel.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste and Mouthwash: Fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash can strengthen the enamel and reduce the risk of decay. Choose a toothpaste that is specifically designed for sensitive teeth, as it can help to desensitize the nerves and reduce sensitivity.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Acidic foods and drinks can erode the enamel and expose the dentin, leading to sensitivity. Avoid consuming citrus fruits, vinegar, and soda and limit your intake of acidic foods to prevent sensitivity.
- Wear a Mouthguard at Night: If you grind your teeth at night, consider wearing a mouthguard to protect the teeth from damage. Teeth grinding can wear away the enamel and cause sensitivity, so wearing a mouthguard can be an effective preventive measure.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help prevent tooth sensitivity. Removing food particles and plaque buildup can reduce the risk of decay and gum recession, leading to sensitivity.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal Disease, also known as gum disease, is a common dental problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures of periodontal disease to help you maintain good oral health.

What Causes Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is a common dental issue that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. There are several causes of periodontal disease, which we will discuss in detail below.
Poor Oral Hygiene:
One of the primary causes of periodontal disease is poor oral hygiene. When brushing and flossing are not done regularly, plaque buildup occurs. Plaque is a clear sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on the teeth. If the plaque is not removed by brushing or flossing, it hardens and forms a substance called tartar. Tartar can only be removed by professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist. Tartar buildup can lead to bacterial infection, which can cause inflammation and damage to the gums.
Bacterial Infection:
The bacteria present in plaque and tartar can cause bacterial infection in the gums. This can lead to various stages of gum disease from gingivitis (gum inflammation) to advanced periodontitis (extensive damage to the supporting bone and tissues that hold teeth in place). The bacterial infection triggers the body’s immune system to fight the infection, leading to inflammation, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
Gum Infections:
Periodontal disease can also be caused by gum infections. The infection can start in the gums and then spread to the surrounding tissues and bone, leading to tooth loss. Gum infections can occur due to plaque and tartar buildup, poor oral hygiene, and other risk factors like hormonal changes in women, certain medications that reduce saliva flow, and misaligned teeth that are difficult to keep clean.
Smoking:
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. It weakens the immune response of the body, making it harder for the body to fight gum infections. Smokers are also more susceptible to plaque and tartar buildup due to reduced blood flow to the gums.
Genetic Factors:
Genetic factors can also play a role in periodontal disease. Some people may be more susceptible to gum disease due to their genetic makeup, regardless of how well they maintain oral hygiene.
Underlying Medical Conditions:
Underlying medical conditions can also increase the risk of gum disease. People who have diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease, as their immune system may not function properly. Other health conditions that affect the immune system or blood flow to the gums can also increase the risk of gum disease.
How Can I Prevent Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common dental problem that affects many people worldwide. It is caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth, which can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums. However, there are several ways to prevent this disease. Here are some tips on how to prevent periodontal disease:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
The best way to prevent periodontal disease is to maintain good oral hygiene habits. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes using fluoride toothpaste can help remove plaque buildup. Flossing at least once a day also helps to remove plaque and food particles from in between the teeth and along the gum line.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental visits are crucial in preventing periodontal disease. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease during routine check-ups and cleanings and can advise you on the best methods to maintain good oral hygiene. It is recommended that you visit your dentist every six months.
- Control Plaque Buildup
Plaque buildup is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease. To control plaque buildup, limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks, and avoid snacking between meals. These practices reduce the amount of bacteria that can accumulate in your mouth and also help to prevent tooth decay.
- Watch Out for Gum Infections
Gum infections are another significant risk factor for periodontal disease. If you notice any signs of gum infection, such as redness, swelling, or bleeding gums, you should see your dentist immediately. Early treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading and causing further damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regular dental checkups are incredibly significant for identifying dental problems at an early stage. As discussed earlier, various dental problems like tooth decay, enamel loss, dry mouth, sensitivity, and periodontal disease can lead to severe complications if left untreated. By visiting a dentist regularly, you can ensure that any potential dental problems are detected and treated early on.
It is essential to emphasize the importance of seeing a dentist on a routine basis to identify dental problems while they are still in their initial stages. If left untreated, they can result in more significant issues, leading to more complicated and expensive treatments.
Therefore, it is quite crucial to prioritize your dental health and make regular dental checkups a priority. Do not wait until you experience pain or discomfort to schedule an appointment. With early identification of dental issues, you can prevent them from becoming severe and affecting your quality of life. Taking care of your dental health is essential to leading a healthy, happy life.…